- Published in Wellness
Breast Milk is the Best
Breast Milk is the Best
By Arturo Gastañaduy, M.D., A&G Pediatrics
Click aqui para español- > La leche materna es la mejor
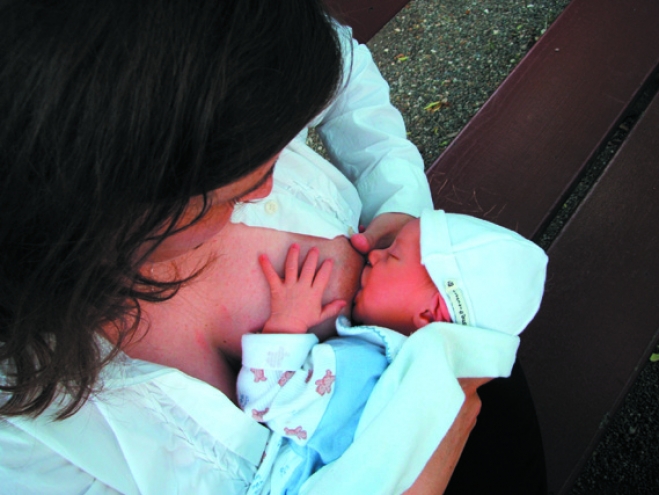
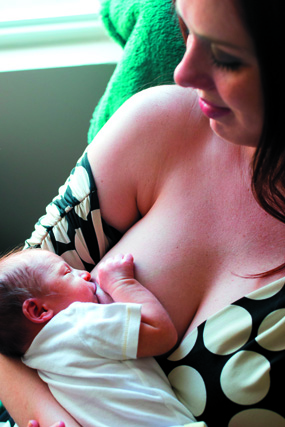
Breast milk is the ideal food for your baby. Exclusively breastfeeding for six months is the optimal way to provide good nutrition to all infants for healthy growth and development. Solid foods should be introduced at six months of age and breastfeeding should continue until the first birthday or beyond. No extra water is required when breast milk is present, and the only additional supplement needed is Vitamin D.
Unlike formula, breast milk boosts the baby’s immune system by providing antibodies, white blood cells and other factors that decrease the risk and severity of infections like colds, pneumonia, ear infections, diarrhea, etc. It also decreases the risk of developing allergies, asthma, eczema, obesity, leukemia and SIDS.
Breastfeeding also promotes mother-infant bonding and stimulates brain development. Infants who are exclusively breast fed for 3 months or longer have higher intelligence scores.
Maternal benefits include lower risk of hypertension, diabetes, breast and ovarian cancers, decreased blood loss after delivery, increased child spacing, and earlier return to pre-pregnancy weight.
Practical advantages of breastfeeding: It is free, always ready at the right temperature, with no need for bottles and sterilizing equipment. Since fathers do not have to get up to fix a bottle in the middle of the night, they can be of use for other tasks!
Despite all the benefits of breast milk, most mothers stop breastfeeding too soon – only 1 in 4 infants is exclusively breastfed for 6 months. Moreover, breastfeeding disparities exist with lower rates among African Americans, young mothers, the southeastern region of the U.S., and rural areas and infants enrolled in the WIC program.
The most important stimulus for milk production is the sucking by the infant. If this is interrupted, milk quantities will decrease. Problems with latching, concerns about the amount of milk produced, sore breast, cracked nipples, early formula feeds, and lack of hospital, family and work support are some of the reasons for early interruption of breast feeding.
Breast feeding contraindications are few and infrequent. Ask your doctor about them.
Tips for parents
Attend pre-natal classes
Choose baby-friendly hospitals for delivery
Ask for skin-to-skin contact immediately after birth
Keep your baby in your room and breastfeed frequently
Steady milk production takes several days.
Initially, only small amount of clear yellow fluid (colostrum) is produced. Colostrum has antibodies and white blood cells that protect your baby against infections.
Be patient with yourself and your baby; he/she needs time to learn to eat.
Avoid formula supplementation, unless medically needed.
No pacifiers; have your baby suck your breast to produce more milk.

























